GST E-Invoicing – A Detailed Guide & All You Need To Know

The quest for an efficacious GST processing system finally came to an end with the introduction of E-invoicing. It means users can generate e-invoices only after the attainment of an IRN or Invoice Reference Number. They need to upload particular particulars in the FORM GST INV-01 on the advised Invoice Registration Portals. The generation of these digital invoices will take place at a common GST Government portal. However, the invoices will not be generated by the Government portal.
With effect, from 1st October 2020 e-invoicing under GST notification makes it compulsory for businesses to produce e-invoice for each & every sale on the Government’s GST portal. The invoicing GST is mandatory for notified classes of listed persons (Businesses whose annual turnover is Rs 500 crore & above in a financial year based on PAN).
The mechanisms of e-invoicing are user-friendly. Users can enjoy benefits like auto-generation of Electronic Way Bill, invoice auto-reporting into GST return, etc. E-invoicing will promote interoperability & standardization that will result in dispute reduction amidst transacting parties. Not just this, but it will enhance payment cycles & reduce processing costs.
It is quite challenging for SMEs to cope with the current GST Regime. The e-invoicing initiative is also meant for businesses that intend to list their businesses under the GST regime but hesitate due to the present difficulties involved. Electronic invoicing under GST is direct & comes with multifaceted support from GST Council. Small businesses can thus largely benefit from the new system.
In this blog, we will learn about the e-invoicing initiative by GSTN (GST Network) that is all set to launch on October 1. E invoicing simply does not refer to invoice generation on the GST portal. In fact, it is the submission of a standard invoice that is already generated on a single e-invoice portal. This leads to the automation of multi-use reporting with just a one-time contribution of invoice details.
What led to the introduction of an e-invoice in the first place?
One of the most common FAQs on e invoicing includes the question, as to why the Government felt the need for an invoicing GST.
When particular accounting software generates raw data & invoices, usually any other software is unable to read it. The human eyes might perceive these as similar but when it comes to machines, the invoices that the other software is generating are absolutely incomprehensible.
For instance, a machine that utilizes a “Tally system” can never read invoices that the SAP system generates. Now, supplementary data entry in every stage will be necessary when a new party accesses the information. The new party will also carry its own auditing software. The extra data entry is slow & is vulnerable to human errors. This called for the designing of a uniform designing system i.e. the E-invoicing system. This is a system that every GST & accounting system will understand.
The introduction of Invoicing in the GST system is also significant for facilitating the speediness of doing business. Most importantly, taxpayer businesses with this new e-invoice system do not need to transform into a new system. In fact, they can use their previous ERP software. The changes that the e-invoice requires are merely on the backend level.
The present system of e-invoicing issuing procedure:
With the help of different kinds of software, businesses currently engender invoices. The GSTR-1 return witnesses the manual uploading of the invoice details. GSTR-A form records this information upon the filing of GSTR-1 by a respective supplier. Looking at the other side, it is mandatory for transporters to generate e-way bills. They can do this by manually importing invoices in JSON or Excel.
The Invoicing in GST e-invoice scheme that will start on October 1 is for businesses whose B2B transaction exceeds the threshold of a turnover of Rs 500 crore. Yogendra Garg who is the CBIC Principal Commissioner stated that this scheme will enhance the current GST return filing procedure due to the new features incorporated.
What are the requisites for being e-invoice ready?
The process of issuing invoices will be the same for businesses even now. The e-invoicing requisite will change in context to enabling invoice reporting to IRP & attaining IRN. The changes will be expedited by Accounting & Billing/ERP software providers in their relevant software. It is critical for them to perceive the updated version consisting of this facility.
Which are the documents that e-invoicing presently covers?
- Debit notes
- B2B invoices
- Credit notes
- Invoices that are issued for exports
As per the GST on invoice initiative, only a category of registered persons will issue the documents. It is true that manifold papers are covered but the entire system is classified as ‘e-invoicing’.
Will B2C business enterprises also need to follow e-invoicing?
E invoicing is not put into effect for B2C invoices. Currently, GST on invoice is only applicable for B2B supplies. It is also for export supplies by a segregated category of registered persons.
Which are the entities that the e-invoice mandate exempts?
- Dealer of passenger transportation service
- Special units of economic
- Goods transport agencies that supply services in context to goods transportation by road in goods carriages
- Insurer or financial institution that incorporates non-banking financial companies as well
What is the need for a user to generate e-invoices?
E invoicing is a system to report the details of an e-invoice in JSON set-up to IRP. The goal is to receive a signed e-invoice in the JSON format right from the portal.
Will the Government offer tools for reporting invoices to IRP?
Government will offer tools to small entities that do not have their respective software solutions. They will be handed over a free offline utility that will help them in creating invoices easily.
What are the manifold e-invoicing generation modes?
Taxpayers will have the liberty of choosing from multiple modes for generating e-invoices. The modes are mentioned as below:
- Mobile application based
- GST Suvidha Provider based
- API based
- Offline tool based
Can a supplier directly generate IRN?
A seller cannot generate an IRN. Only the IRP portal can return it.
Is uploading invoices in bulk to IRP possible?
Large taxpayers can largely benefit from the feature of bulk e-invoice uploading. The ERP they use needs to be designed in a way that they can easily upload the invoices in bulk.
Will a user need to put in the invoice details on the Government website & get the IRN?
- In the context of an e-invoice, ‘machine-to-machine’ invoice data exchange is foreseen. This will take place between the system of the supplier & the IRP.
- Users can obtain IRN by putting in e-invoice data through a web-based screen but this mode will be utilized rarely.
- In the end, this will be substituted by a mobile application based tool for certain taxpayers
What is the e-invoicing initiative by GSTN all about?
The GST Council held its 39th meeting on 20th September 2019. The council approved the new e-invoice format by GSTN linked with ICAI. The format of invoicing GST is at par with international & numerous industry standards. The format even caters to manifold businesses & industries.
Every application provider like Tally or SAP must adhere to the standards set by PEPPOL for the purpose of invoice generation. This will allow taxpayers to produce compliant invoices right at the source. PEPPOL standard is chosen by GSTN as it functions on the Universal Business Language edition of electronic XML.
The elements present in the e-invoice are as follows:
-
E-invoice Schema –
This incorporates technical field names, the narrative of every field, space where the fields are compulsory, some sample values with descriptive notes, etc.
-
Masters –
Here the pre-defined inputs for specific fields by GSTN itself are present. This includes fields such as invoice type, UQC, supply type, State Code, etc.
-
E-invoice template –
This template is according to GST rules. Readers can correlate the various terms put in other sheets with the help of the template.
When is the exact date for the new e-invoicing implementation?
B2B or B2G marketers whose turnover is Rs 500 crore annually can opt for invoicing in GST from 7th January 2020 via APIs. The taxpayers whose turnover threshold is less than Rs 500 crore but Rs 100 crore can generate invoices from 1st February 2020. The e-invoicing under GST was all set to be executed on 1st April 2020. However, the dates are now postponed to 1st October 2020. This is only for taxpayers whose turnover is more than Rs 500 crore. The cumulative turnover will comprise the revenue of every GSTIN underneath a solitary PAN, all over India.
Incentivizing businesses for the adoption of e-invoice generation
In the 39th meeting, the GST Council was strong-willed about the execution of electronic invoice GST under QR code applicability & GST scheme. Given the current coronavirus pandemic, it is all set to begin from 1st October, 2020.
Upon the system generation of e-tax invoice, businesses will no longer need to file their GST returns. This is because auto-filling of the data invoice wise will take place in the return form.
Chief executive of the GST network and officers committee plan to introduce this new e-invoicing initiative for, diminishing invoice compliance & generation burden. The main goal of such initiatives is to keep a check on GST evasion.
Also, it is very surprising that out of 1.21 crore listed businesses, a mere 20 lakh is only eligible for the composition scheme.
As per a tax expert, this electronic invoicing under GST will decrease the manual work in tax returns checking & filing and double efforts as well.
To encourage businesses for the adoption of this new system, the department of tax might also edge the occurrence of compulsory departmental audits.
How will businesses benefit from electronic invoicing?
GSTN’s e-invoice will have the following benefits on businesses:
- There is a major gap present in data reconciliation under the Goods and Services tax for reducing mismatched errors. E-invoice helps in solving this problem.
- E invoice enables real-time invoice tracking that is arranged by suppliers.
- E-invoice boosts the availability of valid input tax credit.
- E-invoices that are generated on particular software can be interpreted by some other. This leads to interoperability & also diminishes errors linked with data entry.
- E-way bills can be auto-generated with the use of e-invoice data
- E-invoicing GST will accelerate the time of invoice delivery
Getting involved with the process of e-invoicing:
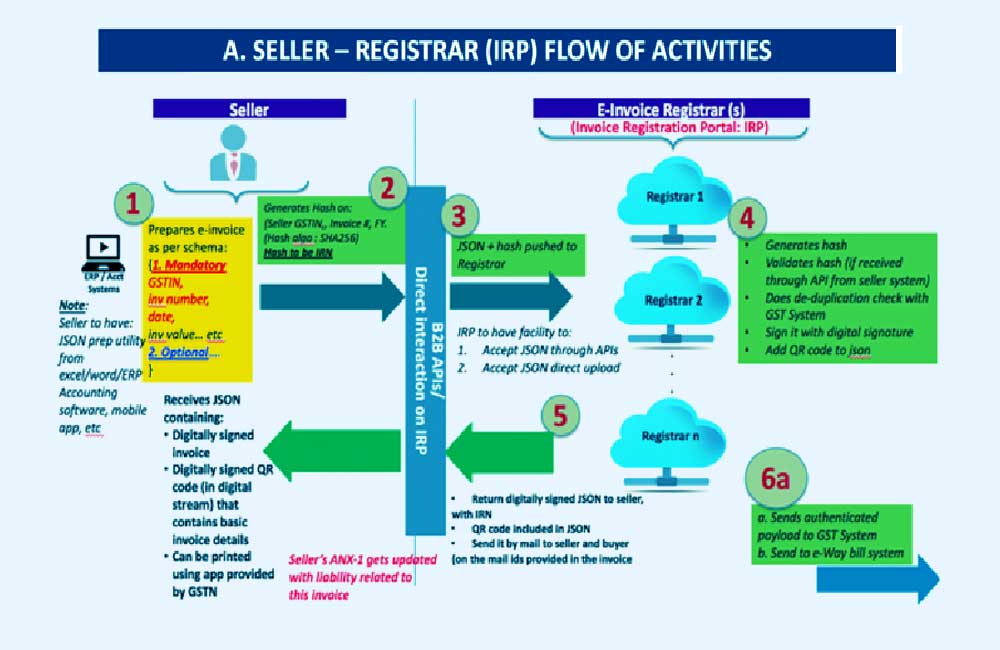
To raise or generate an e-invoice, B2B businesses need to undergo the following stages:
- The taxpayer must utilize the reconstructed ERP system according to the PEPPOL standard. The e-invoicing standards set include e-invoice schema and also CBIC’s mandatory parameters. To incorporate these standards, the taxpayer can synchronize with the appointed software service provider.
- A taxpayer can generate IRN by choosing from these two options:
The computer system’s IP address can be recognized on the electronic invoice portal for straightforward API integration. Other than that, integration through GSP or GST Suvidha provider is also possible.
To upload invoices in bulk, one can download the very helpful Bulk generation tool. It will then produce a JSON file that the taxpayer can upload on the e-invoice portal for generating bulk IRNs.
- Then the taxpayer needs to generate a standard invoice on that particular software. Uploading necessary details such as supplier’s GSTN, item rate, billing address & name, transaction value, applicable GST rate is important.
- On choosing one of the options mentioned above, the taxpayer can generate an invoice on the respective billing software. Uploading invoice details is possible through the JSON file or via direct API. The details of the invoice especially emphasize the compulsory areas of the IRP. The IRP functions as the central registrar for the authentication of e-invoicing. Other modes of IRP interaction are also available like mobile application & SMS based.
The role of IRP is to now:
- Check for plagiarisms
- Produce invoice reference numbers for reference (#)
- Authenticate the key details of each B2B invoice
-
The four parameters depending on which the generation of IRN takes place are:
- Seller GSTIN
- FY in YYYY-YY
- Document type (INV/DN/CN)
- Invoice number
-
IRP also is responsible for:
- Generating the IRN
- Creating QR code for the supplier in Output JSON
- Digitally signing the invoices
- Similarly, sellers will also receive intimation of the generation of e-invoices through email
- IRP will now send the valid payload to the GST portal for the purpose of GST returns. In case if applicable, the e-way bill threshold will also receive the details. The seller’s GSTR-1 obtains auto-filling for the germane tax period. It will in turn keep track of the tax liability.
Taxpayers can keep on printing invoices in the same way it is done with a logo. The electronic invoicing system simply aims to mandate taxpayers for reporting invoices on the IRP & in an electronic format.
What are the changes every taxpayer must determine?
- The accounting system of the taxpayer must prop up the e-invoice requisites.
- After the issuing of an IRN number, it will be traded into the system. It will then capture the IRN that corresponds to the particular tax invoice.
- On the packaging or the dispatch slip, displaying the IRN number is mandatory.
- The last one is to capture the IRN adjacent to the e-way bill present in the system.
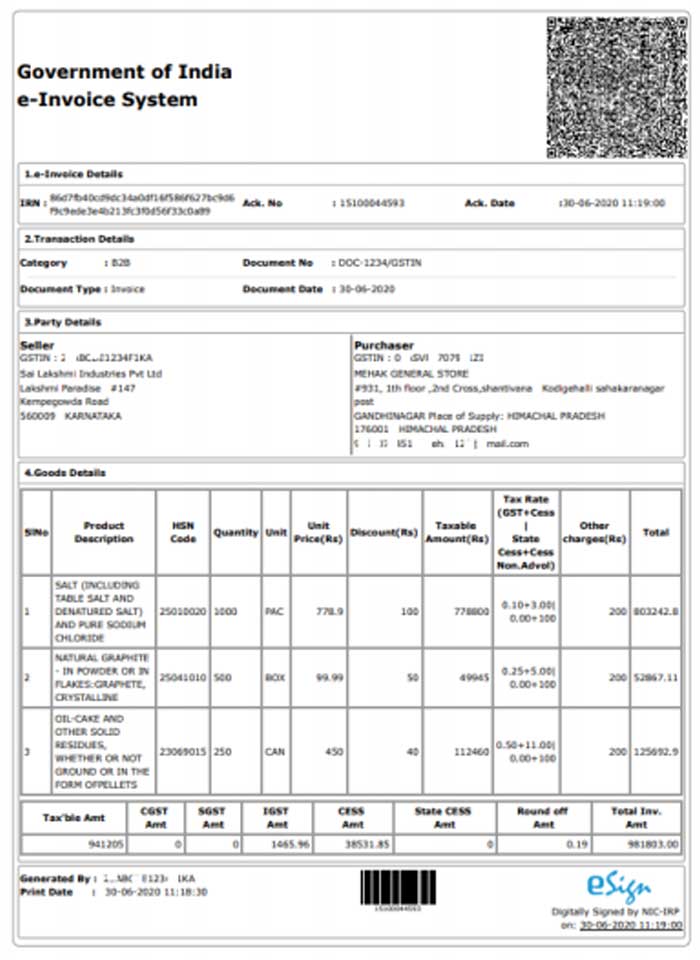
Which are the compulsory fields present in an e-invoice?
It is mandatory for every e-invoice to adhere to the rules presented by the GST invoicing system. Along with this, the e-invoices must also accommodate the policies or invoicing system followed by every sector or industry in India.
The summary of the contents of the recent e-invoice format as reported on 30th July 2020 are:
- 12 sections include optional as well as mandatory areas. There are 6 annexures and these comprise a total of 138 fields
- Out of these 12 sections, 5 are compulsory & 7 are non-compulsory. But the two annexures are obligatory
- The 5 compulsory sections are:
- Basic details
- Supplier information
- Recipient information
- Invoice item details
- Document total
-
The two compulsory annexures are the item details & document total
The fields that must be mentioned in an e-invoice are:
| Sl.No. | Name of the field | List of Choices/Specifications/Sample Inputs | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IRN | Max length: 50 Sample: 649b01ft | This is a unique reference number for the invoice. It can be generated by the seller or can be left blank before submission to IRP. In case IRN is generated by the seller, the system will validate it and register against the invoice. If this field has been left blank, the e-invoice system will generate an IRN. The invoice is valid only if it has IRN and it is registered on the e-invoice system |
| 2 | Invoice_Type_Code | Max length: 10 Can be one of the following: Reg/SEZP/SEZWP/EXP/EXPWP/DEXP | Denotation for regular, SEZ supplies with payment, SEZ supplies without payment, deemed exports, sale from the bonded warehouse, export without payment of tax, and export with payment of tax |
| 3 | Invoice Number | Max length: 16 Sample input is ‘Sa/1/2019’ | For unique identification of the invoice, a sequential number is required within the business context, time-frame, operating systems and records of the supplier. No identification scheme is to be used |
| 4 | Invoice Date | (DD/MM/YYYY) | The date when the invoice was issued |
| 5 | Invoice_Period_Start_Date | (DD/MM/YYYY) | Not explained |
| 6 | Invoice_Period_End_Date | (DD/MM/YYYY) | Not explained |
| 7 | Preceeding_Invoice_Reference | Max length:16 Sample input is ‘Sa/1/2019’ | Detail of original invoice which is being amended by a subsequent document such as a debit and credit note. It is required to keep future expansion of e-versions of credit notes, debit notes and other documents required under GST |
| 8 | Preceeding_Invoice_Date | (DD/MM/YYYY) | The date when the invoice was issued |
| 9 | Supplier_Legal_Name | Max length: 100 | Name as appearing in PAN of the supplier |
| 10 | Supplier_GSTIN | Max length: 15 Must be alphanumeric | GSTIN of the supplier raising the e-invoice |
| 11 | Supplier_Address1 | Max length: 100 | Address of the supplier |
| 12 | Supplier_State | Max length: 50 | State of the supplier |
| 13 | Supplier_Pincode | Max length: 6 | Pincode of the supplier |
| 14 | Billing_Name | Max length: 100 | The trade name of the buyer should be mentioned here |
| 15 | Billing_GSTIN | Max length: 15 | The GSTIN of the buyer to be declared here |
| 16 | Billing_POS | Max length: 2 | The place of supply state code to be declared here |
| 17 | Billing_Address1 | Max length: 100 | The place (locality/district/state) of the buyer on whom the invoice is raised/billed to must be declared here, if any |
| 18 | Billing_State | Max length: 50 | State of the buyer |
| 19 | Billing_Pincode | Max length: 6 | Pincode of the buyer |
| 20 | Payee_Name | Max length: 100 | Name of the person to whom payment is to be made |
| 21 | Payer_Financial_Account | Max length: 18 | Account number of payee |
| 22 | Mode of Payment | Max length: 6 | Cash/Credit/Direct Transfer |
| 23 | Financial_Institution_Branch | Max length: 11 | IFS code must be mentioned here |
| 24 | Dispatch_From_Details | Details about the place from which goods has been dispatched | |
| 25 | List (items) | A group of business terms providing information about the goods and services invoiced | |
| 26 | Tax_Total | Decimal (10,2) | When tax currency code is provided, two instances of the tax total must be present, but only one with tax subtotal |
| 27 | Paid_amount | Decimal (10,2) | The sum of amounts which have been paid in advance. Must be rounded to maximum of two decimals |
| 28 | Amount_due_for_payment | Decimal (10,2) | The outstanding amount that is requested to be paid. Must be rounded to maximum 2 decimals |
| 29 | Tax_Scheme | Max length: 4 | Mandatory element. Usually mentions ‘GST’ |
| 30 | Shipping_To_Name | Max length: 60 | A group of business terms providing information about the address to which goods and services invoiced were or are delivered |
| 31 | Shipping_To_GSTIN | Max length: 100 | A group of business terms providing information about the address to which goods and services invoiced were or are delivered |
| 32 | ShippingTo_Address1 | Max length: 50 | A group of business terms providing information about the address to which goods and services invoiced were or are delivered |
| 33 | ShippingTo_Pincode | Max length: 50 | A group of business terms providing information about the address to which goods and services invoiced were or are delivered. |
| 34 | ShippintTo_State | Max length: 100 | A group of business terms providing information about the address to which goods and services invoiced were or are delivered. |
| 35 | Subsupply Type | Max length: 2 | A group of business terms providing information about the address to which goods and services invoiced were or are delivered. |
| 36 | Transaction Mode | Max length: 2 | A group of business terms providing information about the address to which goods and services invoiced were or are delivered |
| 37 | Company_Name | Max length: 60 | Detail of person and address wherefrom goods are dispatched |
| 38 | Address1 | Max length: 100 | Detail of person and address wherefrom goods are dispatched |
| 39 | State | Max length: 2 | Detail of person and address wherefrom goods are dispatched |
| 40 | Pincode | Max length: 6 | Detail of person and address wherefrom goods are dispatched |
| 41 | SLNO | Integer | Serial Number like 1, 2, 3… |
| 42 | Quantity | Decimal (13,3) | The quantity of items (goods or services) that is charged in the invoice line |
| 43 | Rate | Decimal (10,2) | The number of item units to which the price applies |
| 44 | Assessable Value | Decimal (13,2) | The unit price, exclusive of GST, before subtracting item price discount, cannot be negative |
| 45 | GST Rate | Decimal (3,2) | The GST rate represented as a percentage that applies to the invoiced item |
| 46 | Iamt | Decimal (11,2) | IGST amount as per item |
| 47 | Camt | Decimal (11,2) | CGST amount as per item |
| 48 | Samt | Decimal (11,2) | SGST amount as per item |
| 49 | Total Invoice Value | Decimal (11,2) | The total amount of the invoice with GST. Must be rounded to maximum 2 decimals |
| 50 | Batch Name | Max length: 20 | Batch number details are important to be mentioned for certain set of manufacturers |
Can e-invoicing limit tax evasion?
Definitely limiting tax evasion is largely possible with e-invoicing & in the following steps:
- Firstly, transactions will occur in real-time which will give the tax authorities access to all transactions. Every e-invoice must be spawned via the GST portal.
- This will mean almost zero invoice manipulation as the generation of invoices takes place before the implementation of transactions.
- This will in turn lead to lesser scope for sham GST invoices. Claiming only authentic input tax credit will then be possible as the invoices will only be generated via the GST portal. GSTN can easily keep a check on invalid tax credit claims as input credit can be aligned with the output tax details.
E-invoicing system under GST – a saviour?
The two biggest advantages that B2B ecommerce platforms can attain from GSTN’s e-invoice system are proof & transparency without a doubt. India is a nation where tax fudging is extensive. As invoice tracking in real-time is now possible by both the Government & vendors, it will definitely reduce the uploading of bogus GST invoices. E invoicing definitely paves the way for a robust digital economy.
The commercial & legal challenges associated with e-invoicing are well handled by e-invoicing solution providers. They offer a wide array of e-invoice formats. The solution can execute document exchanging between suppliers & customers as their present standards can differ based on the accounting systems. However, certain e-invoicing software can operate flawlessly with the present accounting system as well. This is how an organization can leverage benefits through ERP. ERP system implementation means that it will be hassle-free for the organisation to incorporate it with the fresh e-invoicing software.
Enterprises can get hands-on avant-garde electronic invoicing software solutions at exactllyERP. The software solutions come with manifold modes that make e-invoice generation seamless. Users can benefit from value additions like GSTR- data, reconciliation in relation to e-way bills, modified e invoicing print templates, etc. To know more, contact us today.